After a short period of decline in incidences, denial of service (DoS), and Distributed denial of service attacks (DDoS) have become rampant once more. Whenever there is a major internet security incident, it mostly means that a DDoS attack occurred. These cybercriminals often target websites, personal accounts, servers, and other services to overload its internet traffic until the victim’s system becomes impassive to legitimate requests.
Virtually every business organization and governmental agencies consistently need the services of ethical hackers to tackle the mounting threats to Cybersecurity. In the modern-day of IT security, Certified Ethical Hackers are invaluable, which is why they work alongside some of the best and largest organizations across industries such as ICT, financial, healthcare, energy, and government, among several others!
Ethical Hacking is a standard requirement for handling DDoS and DoS attacks. The Certified Ethical Hacker (C|EH) training and credentialing program is an esteemed and reliable Ethical Hacking program offered by EC-Council and teaches you everything you need to know about DoS attacks and how to conduct one ethically.
What Is a Denial-Of-Service Attack?
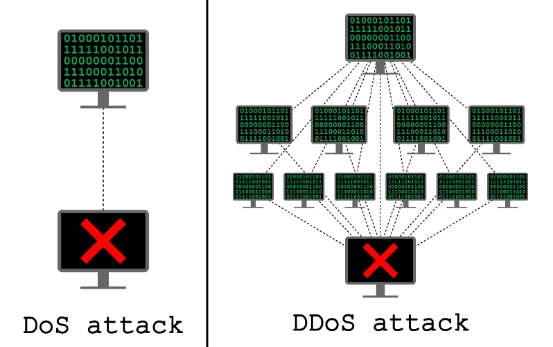
A denial-of-service attack or DoS attack is a type of cyber-attack that occurs when an attacker seeks to render a computer or other networks inaccessible to its authorized users by momentarily or permanently interrupting the normal operations of a host linked to the Internet. Simply put, a denial-of-service (DoS) attack occurs when a cybercriminal prevents an authorized user from retrieving their personal data or files.
Typically, in a DoS attack, a single or group of computers are used to launch an attack. When these attacks are launched, they negatively affect an extensive array of services, including online accounts, private data, emails, websites, and other platforms that depend on the compromised computer or network.
How Do Denial of Service Attacks Work?
A denial of Service attack is often achieved using TCP and UDP packets. In a DoS attack, the perpetrators flood the user’s system with illegal traffic or service requests to inundate its resources and stop it from executing intended tasks.
A DoS attack can target distinct computers or a whole network system. These attacks can be costly for a company, both in terms of finance and timewise, until their services and other affected resources are restored or become accessible.
How to Tell if You are Experiencing a DoS Attack
- The incapability to load certain websites
- The extreme volume of spam emails
- Uncharacteristically slow network performance, including extended load times for files or websites
- Prolonged failure to access specific websites
- A sudden loss of connectivity across devices on the same network
What Is the Most Common Form of DoS attacks?
Smurf Attack :
Here, the perpetrator exploits the broadcast address of a weak network by distributing spoofed packets that belong to the aimed device. Once the receivers of these spoofed packets respond, their Internet Protocol (IP) address is then flooded with those responses.
Considering the fact that a particular Internet Broadcast Address can sustain at most 255 hosts, a smurf attack works by intensifying each ping by 255. The outcome is that the network becomes slow to a level where it becomes difficult to use and discarded.
SYN Flood :
What Is Distributed denial of service (DDoS) Attack With Example?
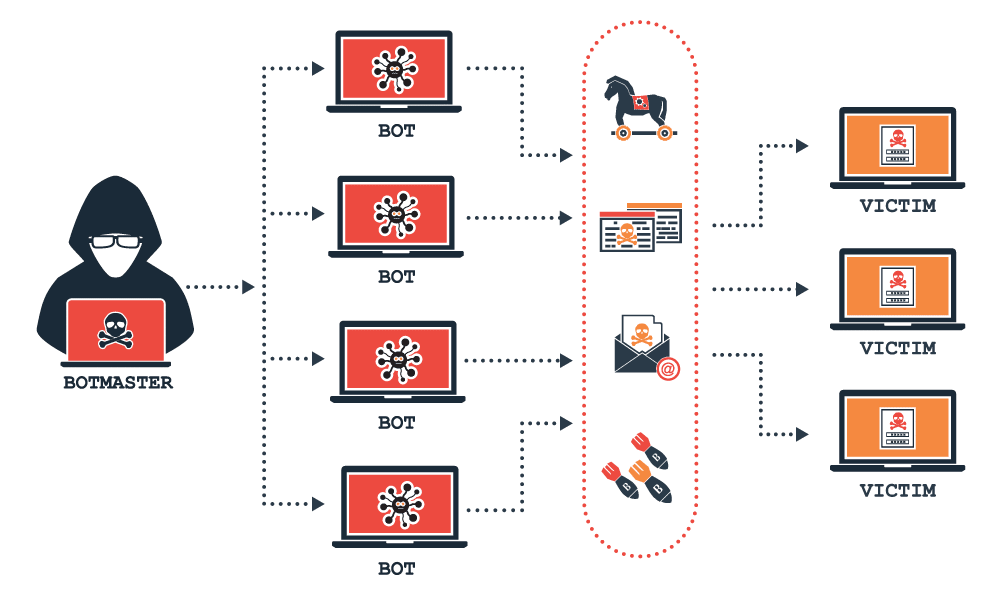
What is a DDoS Botnet?
The term “botnet” refers to a group of hijacked internet-connected devices that are operated remotely from a Command & Control Center (C&C) by a malicious attacker. A botnet is a combination of the word network and robot and each compromised computer is referred to as a bot. These attacks characteristically comprise of unsecured IoT devices, PCs, smartphones, and sometimes resources from public cloud services.
A botnet is designed by a malicious hacker to achieve malicious tasks or execute illegal actions, such as stealing data, sending spam, fraudulently clicking on ads, ransomware, or Distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks. Botnets work by allowing attackers to execute DDoS attacks by seizing the control of several computers and disrupting the traffic source of the traffic. It is often hard for security teams and other security applications to identify a DDoS attack until it is too late.
Malicious hackers use malware and other methods to infect a device, rendering it into a “zombie” in the perpetrator’s botnet. Although some malware may have an immediate effect on the device or network owners, DDoS botnet malware can have diverse stages of visibility. Some of this malware is intended to run mutely as a background while mutely awaiting commands from the “bot herder” or attacker. Other malware is intended to take absolute control of the device or network.
What Is the Difference Between DoS and DDoS Attack?
Broad Categories of DDoS and DoS attacks

Application Layer Attacks
applications to try to exhaust resources, by generating as many transactions and processes as possible. The reason for this approach is, to make the operations initially seem like legitimate requests from users, pending the time when it will be too late, and the victim is inundated and incapable of responding.
These attacks are targeted at the layer where a server creates web pages and reacts to Http requests. The size of this attack is usually calculated in requests per second (RPS), with merely 50 to 100 RPS often needed to bring down a number of mid-sized websites. These attacks involve GET/POST floods, low-and-slow attacks, attacks that target Apache, Windows or OpenBSD vulnerabilities, and Http floods, among others.
Volumetric Attacks

Fragmentation Attacks
Protocol-Based Attack
What Causes Denial of service attacks and
Distributed denial of service attacks?
The most popular motivation for DDoS and DoS attacks is to extort money. The cyber-attacker demands a ransom after sending a crippling DDoS attack. Then, the attacker will promise to halt the attack and restore back the network once a certain amount has been paid. This type of attack is facilitated by the presence of booter services and stresser.
More than a few well-known online software companies have fallen victim to these DDoS attacks, including Vimeo, MeetUp, Basecamp, and Bitly. Some even went temporarily offline, declining the requests of the extortioner.
Hacktivism
Businesses are now using these tools to settle business feuds. Sometimes these attacks are launched to keep a competitor from partaking in a significant business venture. Whereas, other attacks are introduced to completely cripple a business and keep them offline indefinitely.
The motivation for this is to keep the competitor out of service so that their consumers would rush to the opposition. While this is taking place the reputation of the company would be tampered with and they will also encounter huge financial losses.
Business motivated attacks are often well-sponsored and accomplished by experts in the fields. These hackers perform timely investigation and exploit proprietary applications as well as resources to endure tremendously destructive and tenacious DDoS attacks.
How Can Denial of Service (DoS) Affect You
Distributed denial of service and Denial of service attacks are two of the most frightening threats faced by modern-day organizations. Only a few types of attacks can have such detrimental financial impacts as that of a successfully executed DDoS and DoS attack. A recent survey suggested that the average cost of a DDoS attack ranges between 20,000 dollars to 40,000 dollars per hour.
Not only will you be put out of action for a considerable period of time, but a successful DDoS attack can also cause some of your systems to start acting up. With each day you are unable to access your computer and other devices, you begin to incur costs you would otherwise have been spared. This is why you need a Certified Ethical Hacker to safeguard your systems and networks.
How to Stop DDoS and DoS attacks
Monitor Your Traffic
Nearly all DDoS attacks begin with sharp traffic spikes. All these could be symptoms of hackers executing “dry runs” to test your defenses before launching a full-sized attack. So, it would be helpful if you’re able to differentiate between an abrupt surge of genuine visitors and the beginning of a DDoS attack.
Even though your overprovision attempt may not necessarily avert an attack, it will give you some extra time to take deliberate actions before your website become completely saturated.
Make more Bandwidth Available

Monitor your Social media Pages and Public Waste Bins
Consult a Cybersecurity Expert

Create an Effective Incident Response Plan

Managing DoS and DDoS attacks
How to Get the CEH (Master) Credential
C|EH Master is the next progression for the world-recognized Certified Ethical Hacker credential and a logical ‘next step’ for those holding the prestigious certification. Earning the C|EH Master designation is your way of learning, understanding, and putting your knowledge about Ethical Hacking to work.
EC-Council will award the C|EH (Master) certification to you if you clear the C|EH certification and the C|EH (Practical) credential. Ready to become a Certified Ethical Hacker? Click here to complete the C|EH (Practical) exam.












