Information security management is an organization’s approach to ensure the confidentiality, availability, and integrity of IT assets and safeguard them from cyberattacks. A Chief Information Security Officer, IT Operations Manager, or Chief Technical Officer, whose team comprises Security Analysts and IT Operators, may carry out the tasks involved in information security.
It’s obvious that virtually every organization has information they wouldn’t want to be exposed to or wouldn’t want to fall into the wrong hands.
Regardless of whether this data is stored physically or digitally, Information Security Management is crucial to securing the data from being stolen, modified, or other accesses without authorization. You should consider what your organization owns so you can prioritize their protection.
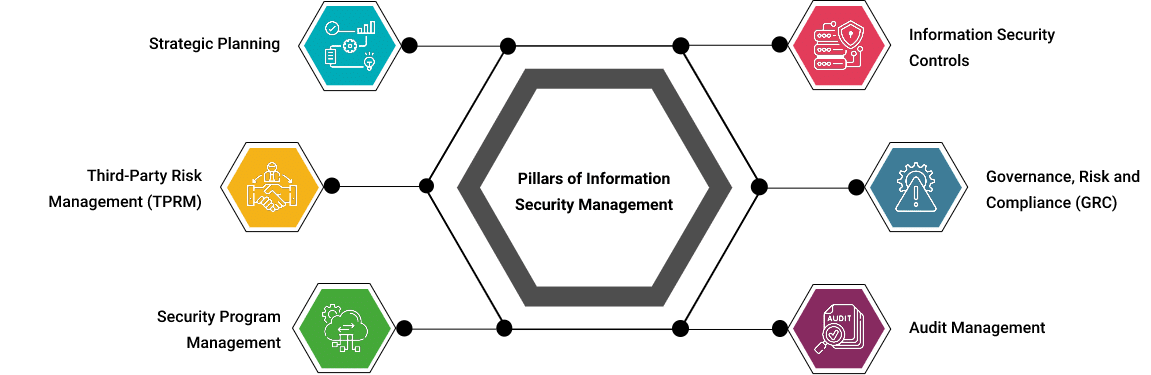
Pillars of Information Security Management
Today, business organizations produce, amass, and store huge amounts of information from their customers, such as credit cards and payment data, behavioral analytics, healthcare information, usage data, and other personal information. All these have increased the threats of cyberattacks and data theft, which has resulted in important developments in the field of information security management.
Information Security Controls
What Are Security Controls?
Types of Security Controls

These are the security measures that the computer system executes, such as firewalls, antivirus software, multi-factor user authentication at login (login), and logical access controls. Technical controls help to prevent unauthorized access or abuse and enable automatic detection of security breaches.
Compliance Controls
Information Security Standards and Control Frameworks
- The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Special Publication 800-53, Security and Privacy Controls for Federal Information Systems and Organizations.
- The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
- The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) standard ISO 27001, Information Security Management.
- The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS).
Relevant training and certification ensure that the leader can implement and execute the Information Security Controls recommended by the council, and perform audits based on the standard. Training makes them familiar with processes and tools used to track/control/prevent/correct use of system and application accounts.
InfoSec professionals who want to take their career to the next level should attempt the leading security risk management courses.
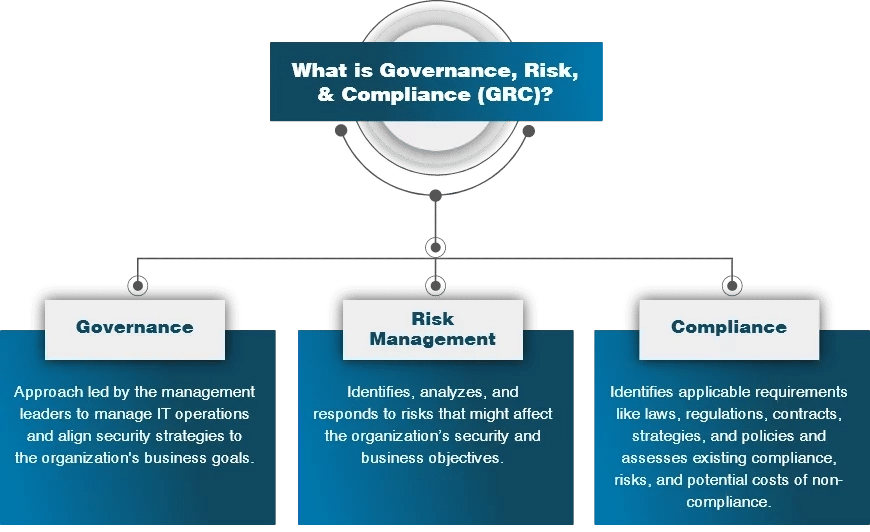
Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC)
Governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) mainly deal with structuring risk management for organizations. Governance and risk management is a strategy that is structured to help you align IT tasks with corporate goals, mitigate risks efficiently, and stay up to speed with compliance.
Governance
What Is Governance?
Best Practices
- Accountability
- Having a competent board
- Having a high level of ethics and integrity
- Outlining roles and responsibilities
- Effectively risk management solutions
- Aligning business strategies with goals
Standards
- The rights of shareholders and key ownership functions
- The appropriate role of all stakeholders in corporate governance
- The equitable treatment of shareholders
- Disclosure and transparency of information about the organization
- The appropriate responsibilities and roles of the board created within the organization
Risk Management
What Is Risk Management?
Risk management involves forecasting and dealing with risks or opportunities linked to your organization’s activities, which could hold back your organization from suitably realizing its aim in uncertain situations. In the cybersecurity environment, risk management is applying a comprehensive IT risk management methodology incorporated into your organization’s enterprise risk management functions.
Types of Risks
- Malware
- Phishing
- Data leakage
- Insider threat
- Hacking
- Zero-day exploits
- DDoS
- MitM Attack
- Trojan Virus
- Social engineering
- SQL injection
Risk Management Process
This refers to the framework for the actions that need to be implemented to mitigate risk. This begins with identifying risks, proceeds to analyze risks, prioritizing risks, treating risk, and finally, monitoring and reviewing the risk.
Principals of Risk Management
- Dynamic
- Integration
- Customized
- Inclusive
- Practices continual improvement
- Considers human and culture factors
- Uses best available information
- Structured and comprehensive
Risk Management Training and Certification
Compliance
What Is Cyber Regulatory and Compliance?
- PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard)
- FedRAMP (Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program)
- FISMA (Federal Information Security Management Act)
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation).
- NY Department of Financial Services (NYDFS) Cybersecurity Regulation (23 NYCRR 500).
- CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act).
- PIPEDA (Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act)
- FERPA (Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act).
- CMMC (Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification).
- Huge financial consequences, litigations, and fines for breaching regulations.
- Access to markets and product delays
- Loss of productivity and revenue.
- Reputational damage
- Government sanctions and license suspensions.
- The risk of injury and potential lawsuits due to an unsafe working environment.
Here are some of the best practices surrounding regulatory compliance
- Determine your end goals
- Understand your industry's regulatory environment
- Create and implement effective policies and procedures
- Identify compliance program improvement opportunities by conducting reviews and evaluations.
- Compliance training
- Establish metrics to measure compliance program improvements
- Conduct a compliance audit
- Track and evaluate the cost of violations
Governance, Risk, and Compliance Training
There are hardly any job roles that don’t benefit from GRC training, including those of an IT Security Analyst, CIO, Business Information Security Officer, Security Engineer or Architect, etc. Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) Training empower security professionals to discover unique insight into GRC activities across the business by fulfilling obligations by enforcing policies. Professionals who have gone through specialized governance, risk, and compliance training are equipped with the tools to help an organization design sound policies.
Cybersecurity Audit Management
What Is Cybersecurity Audit?
Purpose of Cyber Audit

- IFIAR: The International Forum of Independent Audit Regulators established independent audit inspections to enhance the level of audit quality.
- FASB: The Securities and Exchange Commission accepts the Financial Accounting Standards Board as the chosen accounting standard setter for public companies.
- PCAOB: through the establishment of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board, the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 halted the auditing profession's self-regulation framework to oversee the profession.
- GAAS: The Generally Accepted Auditing Standards are the set of systematic regulations implemented by auditors when performing audits on an organization’s financial records.
Security Program Management

- Security policy development
- Risk management
- Incident handling & response
- Security architecture
- Threats & vulnerability

The information security officer training program or certification should also focus on information security projects that include integrating security requirements into other operational processes. Security program management is like a day to day responsibility of a CISO. Such certifications help the security leader understand the security maturity levels, how security engages with the business, its strategy overall and the business goals. It enables the leader to create a security road map and define exactly where they need to set their security benchmark.
Vendor Risk Management (VRM) OR Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM)
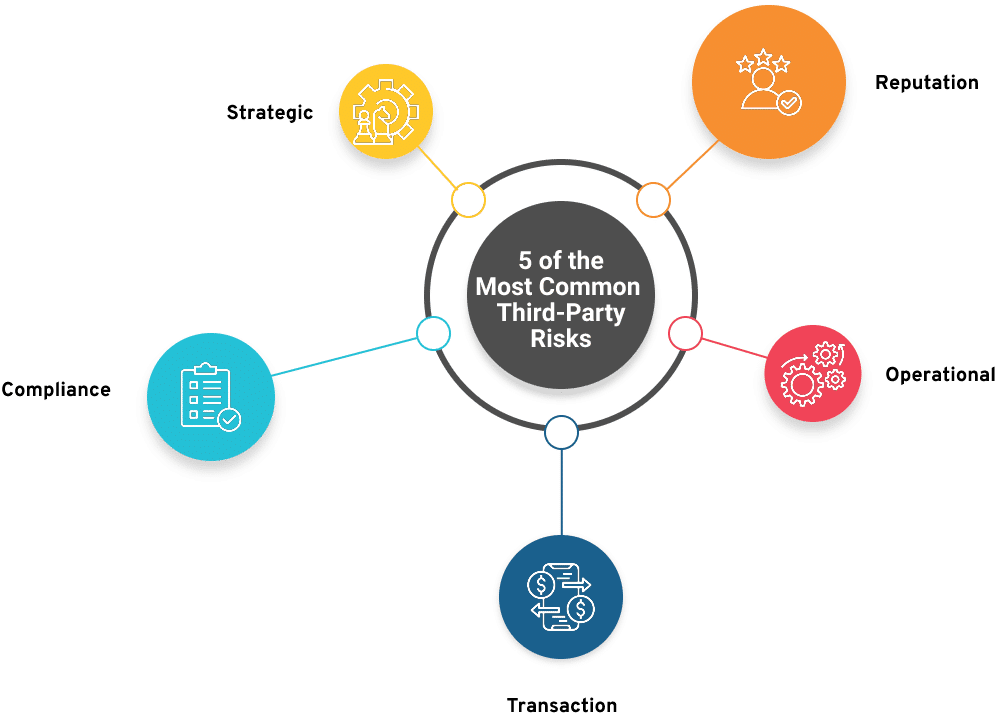
What Is Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM)?
TPRM is an assessment of vendor risk introduced by a firm’s third-party relationships along the whole supply chain. It involves identifying, evaluating, and monitoring the risks represented throughout the lifecycle of your relationships with third-parties. This often begins during procurement and reaches the end of the offboarding process.
Types of Risks while Onboarding Vendors
- Operational risk: Example includes a data breach.
- Regulatory risk: You could pay the price if a vendor violates the law or organizational policy
- Reputational risk: For instance, a rug company outsources production to a factory that violates child labor regulations, resulting in penalties and destructive publicity.
How to Select a Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) Framework?
Best Practices Around Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM)?
You can identify risks at different levels of engagement with third parties. This can be done through penetration testing, threat modeling, red teaming assessment, and so on.
Does Your Business need Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM)?
Vendor / Third-Party Risk Management Training & Certification
Strategic Planning
Aligning Cybersecurity Initiatives with Business Objectives
Aligning your cybersecurity initiatives with your business objectives begins with understanding, describing, and ultimately aligning the relationship between your critical business functions, IT assets, and data.
When you take a careful look at how these components are interconnected, you’ll find it easier to determine which security controls you should apply for each of them. You should also note that business functions will depend on IT assets, IT assets will produce data, and data will provide business functions
Trends in Cybersecurity
- There’s increasing recognition of the significance of cybersecurity solutions
- Data breaches continue to be the top cyberthreat
- Risks associated with IoT devices
- Demand for cybersecurity personnel remain above supply even though IT teams have to handle more security threats than ever before
- Automation and integration in cybersecurity are becoming a necessity
- Cloud-based security issues continue to grow
- AI on both sides of the barricade
- Mobile devices as a major cybersecurity risk
- Phishing attacks remain a constant threat
- The growing impact of state-sponsored cyber-attacks
Return on Investment (ROI)
Vendor Management
Role of a CISO in Managing Information Security Operations
The CISO is the executive-level manager responsible for directing operations, strategy, and the budget needed to ensure and manage the enterprise information assets’ security. The role of a CISO will cover communications, identity and access management, applications, infrastructure, and the procedures and policies that apply.
CISO an Integral part of Business Enablement Process
- Cloud computing
- Mergers and acquisition
- Product security
- Mobile technology
- Emerging technologies
Why CCISO?
- Governance and Risk Management
- Information Security Controls, Compliance, and Audit Management
- Security Program Management & Operations
- Information Security Core Competencies
- Strategic Planning, Finance, Procurement, and Vendor Manage
Sign-up now to begin your information security journey!

Accredited by ANSI

Written by Seasoned Experts

Acknowledges the Value of Real-World Experience












