“With a successful incident response program, damage can be mitigated or avoided altogether.”
Why Is Incident Response Important?
- Restoring daily business operations
- Minimizing financial and reputational losses
- Fixing cyber vulnerabilities comprehensively and quickly
- Strengthening security posture to avoid future attacks
HIPAA (for the healthcare industry)
The Health Insurance Probability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is designed to safeguard Protected Health Information (PHI) stored in an electronic form. Being HIPAA compliant, the healthcare institutions follow the HIPAA Security Rule and ensure to implement administrative, technical, and physical safeguards, thus, protect sensitive personal and health information.
To learn more: HIPAA: All That You Should Know
PCI DSS (for payment industry)
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is a security standard with the primary objective of protecting credit and debit card transactions against data theft and fraud. Even though PCI DSS compliance is not mandatory, businesses should follow their guidelines to secure their credit and debit card transactions. Being PCI DSS compliant helps in building trust relationships with stakeholders and customers.
To learn more: A Introduction to PCI DSS
Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (for the financial services industry)
Gramm–Leach–Bliley Act (GLBA) is an act that helps in improving competition in the industry. Its main aim is to ensure security and confidentiality of customer data, safeguard integrity by protection against potential cyber threats and unauthorized access, and proper disposal of customer data.
To learn more: All About Gramm- Leach-Bliley Act
FISMA (for federal agencies)
The Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA) is a comprehensive framework applicable to US-based federal agencies. The act protects government information, operations, and information assets against natural disasters and cyberattacks.
To learn more: Federal Information Security Management Act of 2002
What are the common types of incidents?

Phishing attacks

Denial-of-Service attacks
Ransomware attacks
SQL injections

Malware attacks
Incident Handling Vs. Incident Management Vs. Incident Response
INCIDENT RESPONSE
INCIDENT RESPONSE
INCIDENT RESPONSE
Incident Management and Business Continuity
What is an Incident Response Plan?
Why should you have an Incident Response Plan?
What should an incident response plan include?
Initial Response Statistics
Reporting
Feedback
To know more about the incident response in a distributed workforce using cloud forensics, check out this amazing video by Michael Weeks, Lead Incident Response Engineer at FICO.
What is an Incident Response Process?
An incident response process helps an organization to remain in business. It is an accumulation of various procedures targeted at identifying, analyzing, and responding to potential security incidents. The primary objective of the process is to minimize the impact and offer rapid recovery.
In simple words, incident response methodology handles security incidents, breaches, and possible cyber threats. It comes with an incident response plan designed to identify the cyber-attack, minimize its impact, and reduce the financial burden.
How is Incident Response Process (OODA Loop) Different from NIST Incident Response Life Cycle?
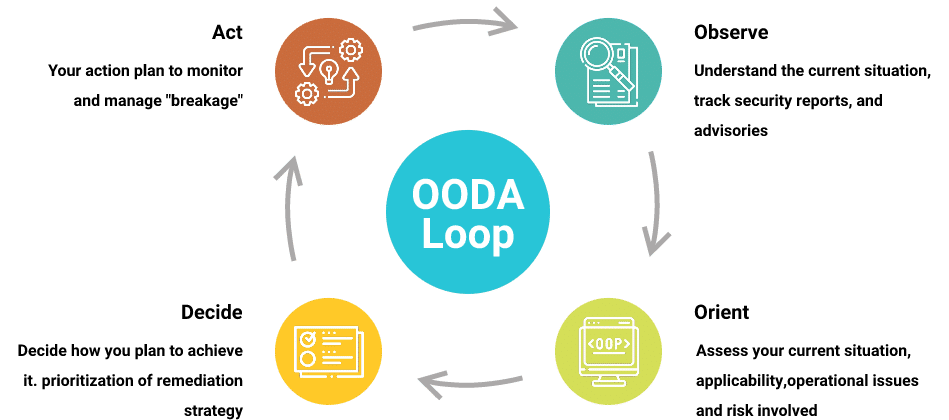
What are the phases of the incident response lifecycle defined by NIST?
Take a look at the five phases of incident response:
What are the five steps of an incident response plan?
What are the five steps of an incident response plan?

Determine the critical components of the network

Identify points of failure in the network and address them

Develop a workforce continuity plan

Form a cyber security incident response plan

Staff training
What is an Incident Response Team?
A computer security incident response team (CSIRT) helps in mitigating the impact of security threats. With the rising number of security threats, organizations need a dedicated team for incident response.
- Create and maintain an IR plan
- Analyze the security incident
- Manage internal communications and alerts whenever an incident occurs
- Offer easy communication with stakeholders and the press whenever needed
- Remediate incident
- Recommend tools, technologies, policy, and governance after the incident
How to build an incident response team?
- Incident Response Manager: The manager supervises the entire process and prioritizes the actions during the detection, analysis, containment, and recovery phases.
- Security Analysts: These professionals work to recover the affected network. There are two types of security analysts in an IR team –
- Triage Analysts – They look for potential threats and filter out false positives.
- Forensic Analysts – They keep digital evidence preserved to conduct forensic investigation against the incident.
- Threat Researchers: They offer threat intelligence and context related to the incident.
Also check out: 5 Common Challenges Incident Handling and Response Teams Face
Professional Tools Used in Incident Response
Businesses are facing a rise in security incidents. In the technologically driven world, these incidents have become unavoidable. That is why the incident response team needs powerful tools to defeat and contain security events.
Security incidents are capable of crippling a business. They can lead to financial loss, reputational loss, negative publicity, and even a negative impact on the sales and stock market. It can strip down an organization from its long-earned credibility. With the help of tools, incident responders can quickly detect, analyze, and respond to intrusions.
Best Incident Response Tools
Incident Response Jobs
Incident Response Manager Jobs
Security Analysts Jobs
Triage Analysts Jobs
Forensic Analysts Jobs
Threat Intelligence Researchers Jobs
Forensic Analysts Jobs

Average Salary of an Incident Handler
The fluctuation in salary relies on a few factors, such as the qualification and skills of the candidate. An expertise in several incident response tools helps an incident responder earn more. Apart from that, the location of work can also have an impact on earning.